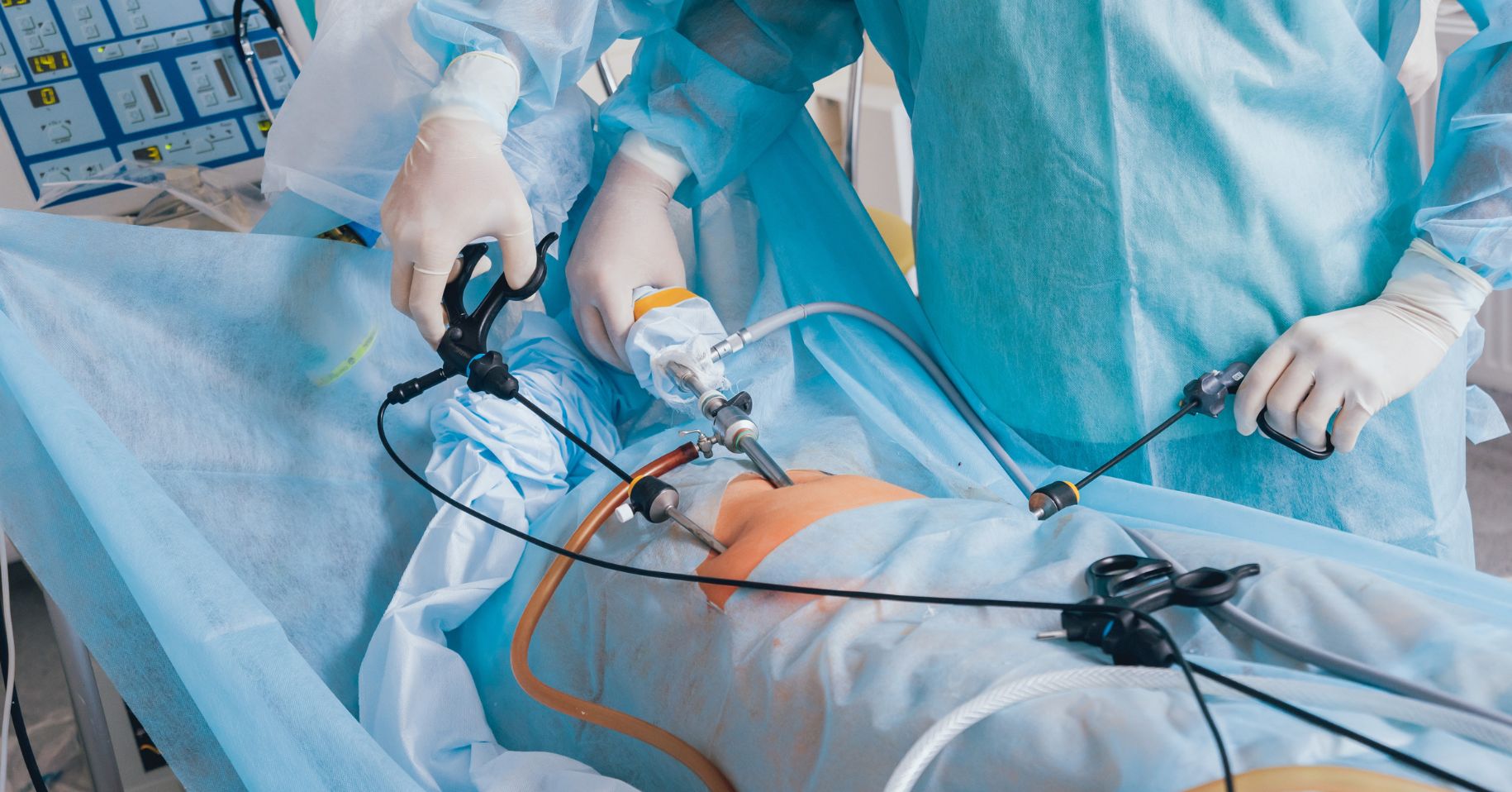
Bariatric surgery includes several procedures designed to aid weight loss by restricting stomach size or altering digestion. Common types are gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion. Each procedure varies in complexity, effectiveness, and suitability based on patient health, weight loss goals, and medical conditions.
-
Working Hours: 05.00PM - 09.00PM
-
Email : contactsupraclinic@gmail.comEmail : contactsupraclinic@gmail.com
-
Phone Number : +91 9347665652Phone Number : +91 9347665652